A negative or positive scan can help give you and your doctor clarity to move forward
During your follow-up appointment, your doctor will review your Neuraceq® PET scan along with results from other tests to figure out whether your cognitive impairment may be due to AD or something else.
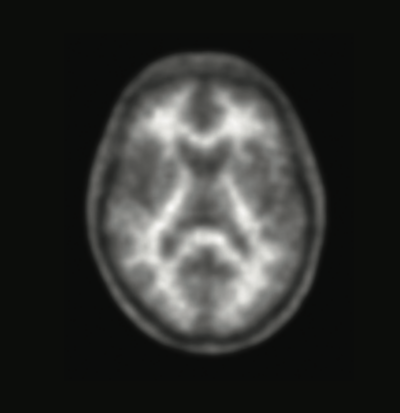
A negative scan
If the Neuraceq® scan is negative, your doctor may consider different causes of cognitive impairment that are not due to AD.
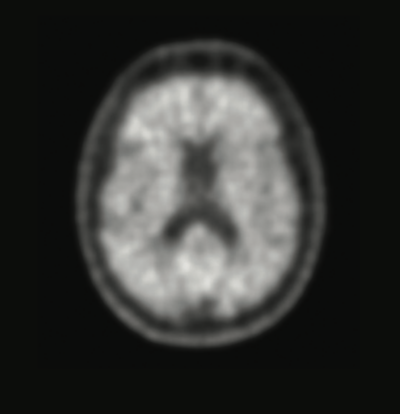
A positive scan
If the Neuraceq® scan is positive, it can help your doctor figure out if you have AD. β-amyloid neuritic plaques are sticky clumps of protein that form in the brains of people who have AD. However, β-amyloid plaques may also be present in other diseases and in people without cognitive symptoms. These plaques affect the way the brain works. The presence of β‐amyloid plaques is a key component for the confirmation of AD.


